Present conditional:
In a present conditional sentence, the if–clause states a particular activity or situation (a condition). The result-clause states a fact or observation as the result of the situation in the if–clause. The present tense is used in both clauses.Important If / When
Both "if" and "when" are used in the Present Real Conditional. Using "if" suggests that something happens less frequently. Using "when" suggests that something happens regularly.
Examples:
- When I have a day off from work, I usually go to the beach.
- If I have a day off from work, I usually go to the beach.
When the if clause comes first, it is followed by a comma. Then is usually ommited before the main clause, but it is always implied.
Example:
If I'm on time, (then) I walk to work
When the main clause is first, there is no comma and then is not used. The meaning is the same.
Example:
I walk to work if I'm on time.
Future conditional:
n a future conditional sentence, the result-clause states a prediction as the result of the situation in the if- clause. The simple present tense is used in the if–clause, and a modal (will, can, may, might, shall) is used in the result-clause.
If and Unless
Sentences with unless in the dependent clause often have the same meaning as sentences with negative if clause.
Unless
Unless the cab comes at three, you wont make it to the airport.
Unless you finish your work, We will lose the account
If
If the cab doesn't come at three, you won't make it to the airport
If you don't finish your work, we will lose the account.
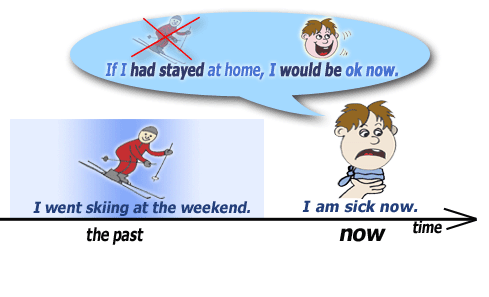
Present and future unreal conditionals:
IF + SIMPLE PAST (THEN) WOULD, COULD OR MIGHT +VERB
We can use it to talk about something in the present which is impossible, because it's not true.
- If I had his number, I would call him. (I don't have his number now, so it's impossible for me to call him).
- If I were you, I wouldn't go out with that man.
Giving advice and opinions
Unreal conditionals beginning with If I were you can be used as an indirect way of giving advice. Unreal conditionals sound softer than modals like should or ought to.
Advice with unreal conditionals
If I were you I'd speak to the instructor.
Advice with modals
You should speak to the instructor.
Asking permission
Unreal conditionals with would you mind, would it bother you, or would it be OK can be used to ask for permission. Notice that a negative response to the first two questions means you are giving permission.
Permission with unreal conditionals
Would you mind if I opened the window?
No, go right ahead
Permission with modals
May I open the window?
Yes, go right ahead
Wishes
wish clause that clause
Simple present (that+) past form
I wish (that) I were older
I wish (that) I didn't have a cold
Use wish to express a desire for something that does not exist now. It is a desire to change a real situation into an unreal or impossible one. As in unreal conditional sentences, the past form does not indicate past time, it indicates that the situation is unreal. The past form can be simple past, past continuous, could or would.
Wishes about the present
I wish I were living in chicago
I wish I could swim, but I can't
Wishes about the future
I wish you would come with me tonight
I wish You were coming with me tonight
I wish you could come with me tonight
Using If only
sentences with If only often have a similar meaning to sentences with wish, but they are more empathic.
VIDEOS






No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario